In the vast landscape of pipe options for industrial applications, the choices can be overwhelming. Understanding the differences between SSAW (Submerged Arc Welding) pipes, LSAW (Longitudinal Submerged Arc Welding) pipes, and ERW (Electric Resistance Welding) pipes is crucial for making informed decisions in various projects.
Pipes form the backbone of many industries, serving as conduits for liquids, gases, and other materials. Each type of pipe has its own set of characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications. In this article, we'll explore the distinctions between SSAW, LSAW, and ERW pipes, shedding light on their unique features and applications.
SSAW pipes, also known as spiral submerged arc welded pipes, are manufactured using a spiral welding process. This method ensures a consistent and uniform weld, contributing to the pipe's structural integrity.
One of the notable advantages of SSAW pipes is their ability to withstand high pressure. This makes them ideal for transporting fluids in challenging environments. Additionally, the spiral welding process allows for a larger diameter, increasing the overall capacity of the pipe.
SSAW pipes find their applications in various industries, including oil and gas, water transport, and structural construction. Their versatility makes them a popular choice for projects with diverse requirements.
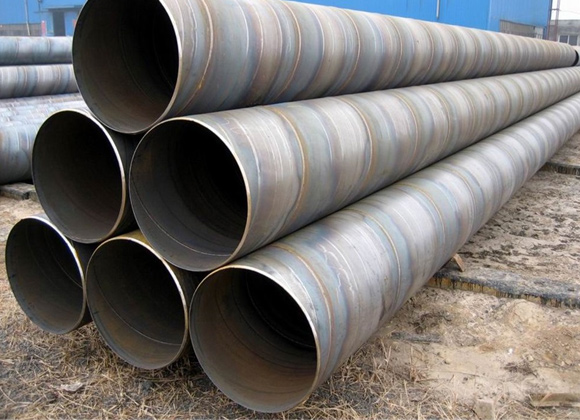

LSAW pipes are crafted using a longitudinal welding process. This technique involves the use of a large plate, which is cold-formed into the desired shape before being welded.
LSAW steel pipe is known for its high strength and exceptional performance in harsh conditions. The longitudinal welding ensures a strong bond, making these pipes suitable for applications where structural integrity is paramount.
The robust nature of LSAW pipes makes them a preferred choice in industries such as construction, shipbuilding, and infrastructure development. Their durability and reliability contribute to their widespread use in demanding projects.
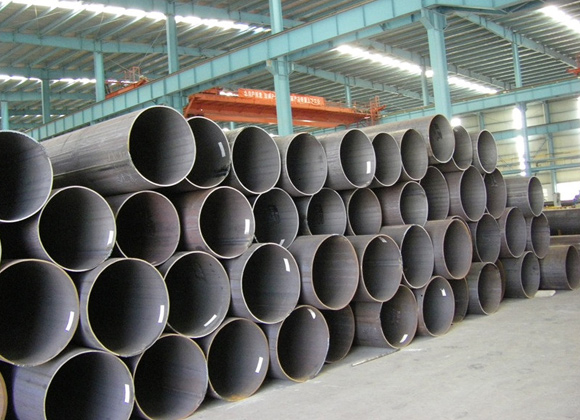

ERW pipes are produced using the electric resistance welding method. In this process, the edges of the steel plate or coil are heated and fused together, creating a seamless joint.
ERW pipes are known for their precision and high-quality finish. The lack of a welding seam along the length of the pipe enhances its strength and reliability. ERW pipes are commonly used for low to medium-pressure applications.
The versatility of ERW pipes makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including plumbing, fencing, and infrastructure projects. Their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation contribute to their popularity in various industries.
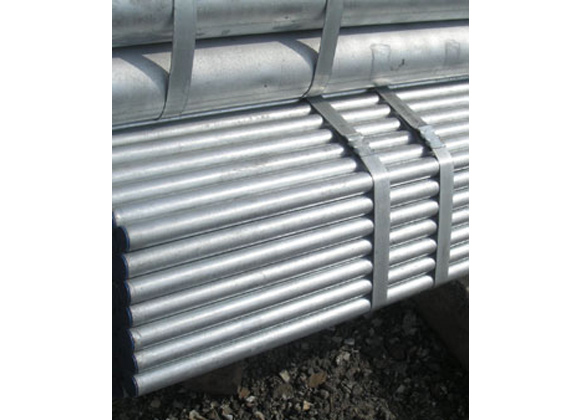

While all three types of pipes involve welding, the specific processes differ significantly. SSAW pipes use a spiral welding technique, LSAW pipes utilize longitudinal welding, and ERW pipes are produced through electric resistance welding. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the right pipe for a given project.
The structural differences among SSAW, LSAW, and ERW pipes impact their performance in different environments. SSAW pipes, with their spiral welds, offer enhanced strength, while LSAW pipes, with longitudinal welds, provide durability in challenging conditions. ERW pipes, with seamless joints, excel in applications with lower pressure requirements.
Consideration of the specific conditions in which the pipes will operate is paramount. SSAW pipes are suitable for high-pressure environments, LSAW pipes excel in harsh conditions, and ERW pipes are ideal for applications with lower pressure requirements. Matching the pipe to the project's conditions ensures optimal performance and longevity.
 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No.68 Hezuo Road, Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Province, China
No.68 Hezuo Road, Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Province, China 